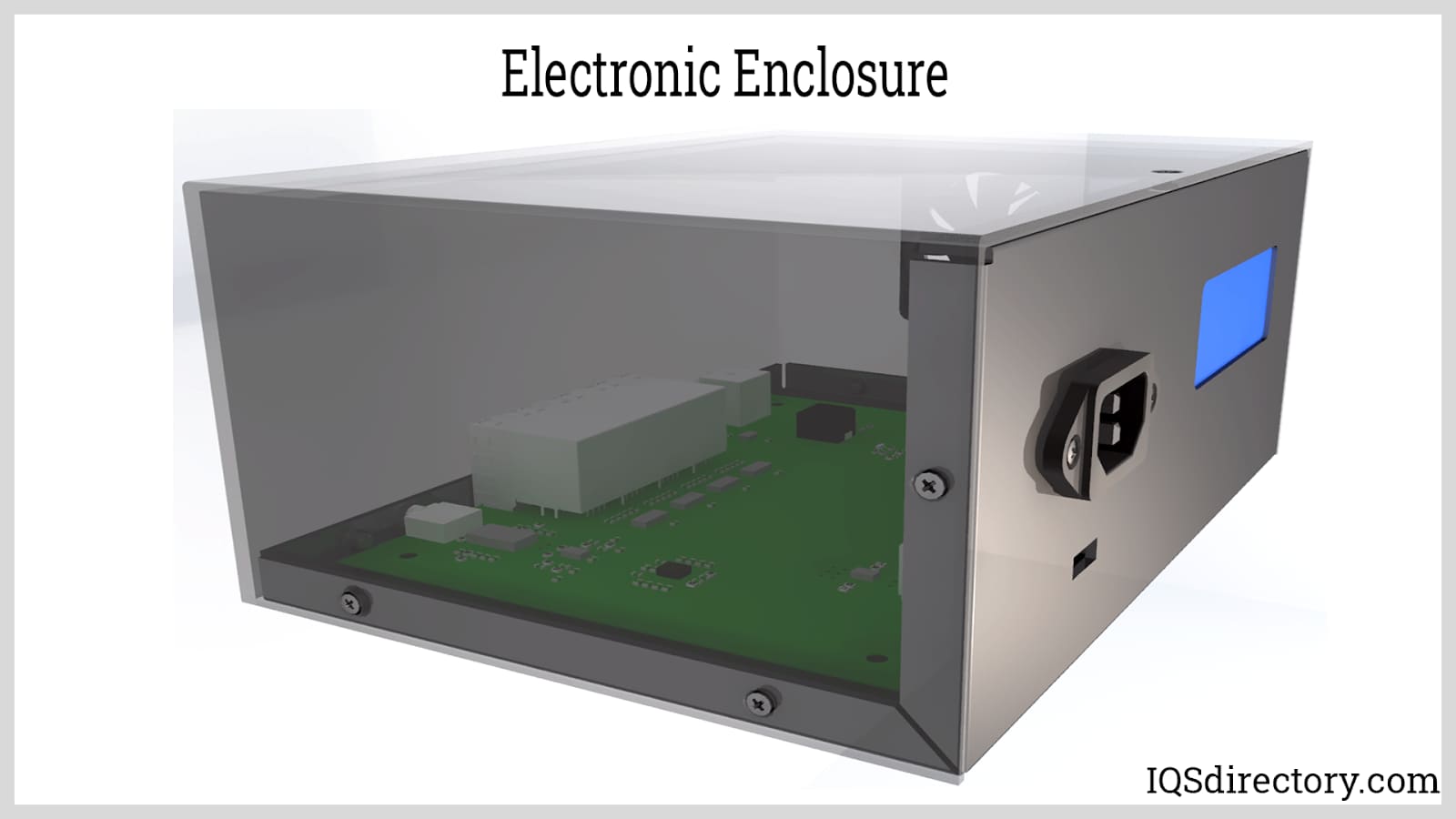
Electronic enclosures, also known as electrical enclosures or electronic enclosure boxes, are boxes that protect electronic equipment such as conduits, connections, and switches from the environment and from tampering. They are found in public places such as street corners or parks as well as in buildings and residences. Read More…
At Hubbell Wiegmann, we specialize in designing and manufacturing high-quality electronic enclosures that protect and support a wide range of industrial and commercial systems. We bring decades of engineering expertise to every product we create, ensuring that our enclosures meet rigorous performance standards while adapting to the evolving needs of our customers.
AutomationDirect.com takes pride in being a trusted partner for businesses seeking reliable electronic enclosure solutions. Our team is dedicated to providing exceptional customer service and technical support to ensure that our customers find the perfect products to meet their needs.
At Ometek Inc., we specialize in designing and manufacturing high-quality industrial electronic enclosures for a wide range of applications. Our team of skilled engineers and technicians has years of experience in the industry, and we are committed to delivering the most reliable and durable enclosures to our customers.
At Accurate Metal Fabricating, we specialize in crafting precision-engineered electronic enclosures that meet the unique demands of modern industries. With a relentless commitment to quality, we pride ourselves on providing cutting-edge enclosures that safeguard electronic components with unparalleled accuracy. At the heart of our success is a passion for innovation, driving us to create...
At Bison ProFab, we specialize in designing and manufacturing high-quality electronic enclosures that deliver superior protection in the most demanding environments. We take pride in our ability to engineer enclosures that meet rigorous industry standards while adapting to the specific needs of our customers across a broad range of applications.

More Electronic Enclosure Manufacturers
Applications
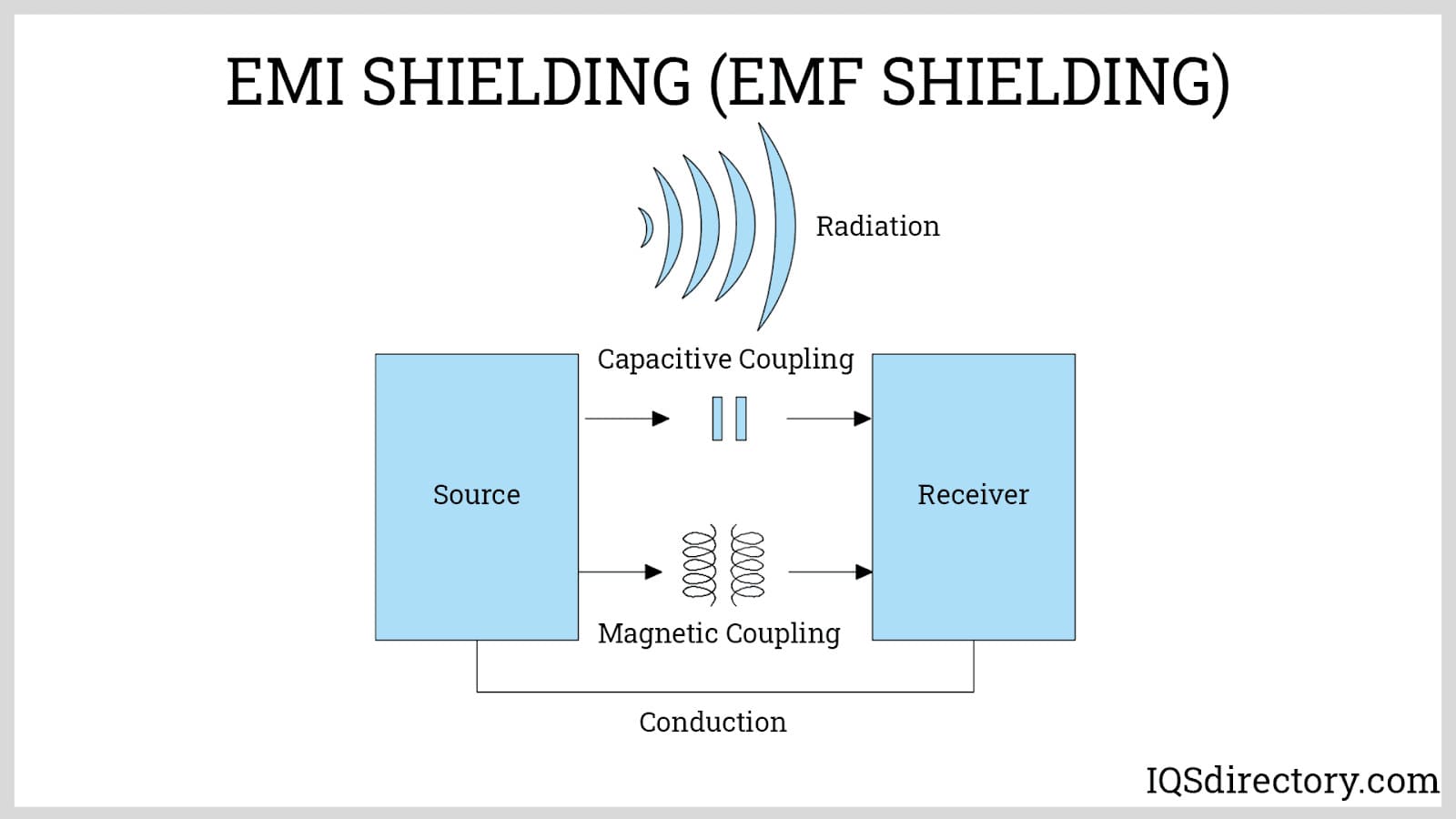
Electronic enclosures are a fundamental component in modern electrical engineering, providing critical protection for sensitive electronic equipment and circuit assemblies. These protective housings, often referred to as electrical cabinets or electrical enclosures, serve as the first line of defense against physical hazards, environmental contaminants, and unwanted electromagnetic interference (EMI). Their robust construction helps prevent damage from dust, moisture, chemicals, and physical impacts, while also shielding delicate internal circuitry from signal disruptions caused by EMI and radio frequency interference (RFI).
Across a diverse range of industries—including medical device manufacturing, automotive engineering, industrial automation, telecommunications, aerospace, defense, agriculture, energy, and consumer electronics—electronic enclosure solutions are indispensable. From safeguarding programmable logic controllers (PLCs) in automated production lines to protecting instrumentation in harsh outdoor environments, these enclosures ensure reliable operation and extended service life of vital equipment. In data centers, rack mount enclosures keep servers cool and secure, while in the healthcare sector, specialized enclosures maintain sterility and protect diagnostic imaging equipment from contaminants.
Are you looking for specific enclosure solutions for your industry? Explore:
- What type of enclosure is best for outdoor telecommunications equipment?
- How do industrial enclosures enhance machine safety on factory floors?
- What are the best enclosure materials for medical electronics?
- How do electronic enclosures support compliance with industry regulations?
Whether you require an enclosure for a ruggedized industrial control panel, a compact IoT sensor, or a high-density server rack, the right electronic enclosure will provide tailored protection, improve safety, and maximize uptime for your application.
History
Electronic enclosures have evolved in tandem with the history of electrical power and electronics. Their inception dates back to the earliest days of electrical distribution, when engineers sought ways to contain and isolate primitive switchgear—then called cut-outs. Early installations left live wires exposed, posing significant safety risks and making critical systems vulnerable to dust, chemicals, and accidental impact. To mitigate these dangers, engineers first encased components in wooden boxes, which were soon dubbed cut-out boxes and became the standard for switchboards and wiring terminations.
However, as electrification expanded into homes and commercial buildings, the limitations of wood quickly became apparent. Wooden enclosures, while easy to fabricate, were prone to overheating, moisture absorption, and even fire when wires became loose or short-circuited. This spurred the development of more robust, flame-retardant metallic enclosures—typically steel or aluminum—which dramatically improved fire safety, electrical insulation, and long-term durability. Over time, new materials like high-impact plastics, fiberglass, and polycarbonate further expanded enclosure options, supporting more complex electronics and environments.
Today, the field of enclosure manufacturing is characterized by innovation—spanning everything from modular server cabinets for cloud computing to explosion-proof housings for petrochemical plants. As the world’s reliance on electronics continues to increase, demand for advanced enclosure technology—offering improved ingress protection (IP) ratings, enhanced EMI shielding, and compliance with global safety standards—continues to surge. Manufacturers now focus not only on protection, but also on ease of access, modularity, thermal management, and aesthetics.
Types of Electronic Enclosures
Choosing the right enclosure is crucial to ensuring the safety, reliability, and performance of your electronic systems. There is a wide variety of enclosure types, each engineered for particular use cases, environmental hazards, and operational requirements. Below is a comprehensive guide to the most common and specialized enclosure types available in the market.
- Mounted Enclosures: Also known as wall-mounted or surface-mounted cabinets, these enclosures are designed for efficient space utilization and easy accessibility. Pre-drilled holes at the base or rear allow for secure attachment to walls or machinery frames, making them ideal for control panels, junction boxes, and security systems in commercial and industrial environments.
- Standardized Rack Mount Enclosures: Engineered for housing standard 19-inch rack equipment, these enclosures are a mainstay in IT infrastructure, audio-visual installations, and laboratory setups. Their modular frames, constructed from steel or aluminum, accommodate multiple electronic modules, servers, and networking devices. Many feature lockable doors, integrated cable management, and optional cooling fans for optimal performance.
- Computer Enclosures: These rugged housings protect computer hardware from dust, accidental impact, and EMI. Available in desktop, tower, and rack-mountable formats, computer enclosures often include EMI shielding, anti-static coatings, filtered ventilation, and tamper-resistant features, supporting both industrial PCs and mission-critical server hardware.
- Electronic Instrument Enclosures: Designed for sensitive test instruments, sensors, and process controllers, these enclosures are crafted to withstand harsh environments including extreme temperatures, vibrations, and chemical exposure. Popular materials include die-cast aluminum, stainless steel, and impact-resistant plastics, available in form factors ranging from handheld and benchtop units to weatherproof outdoor housings.
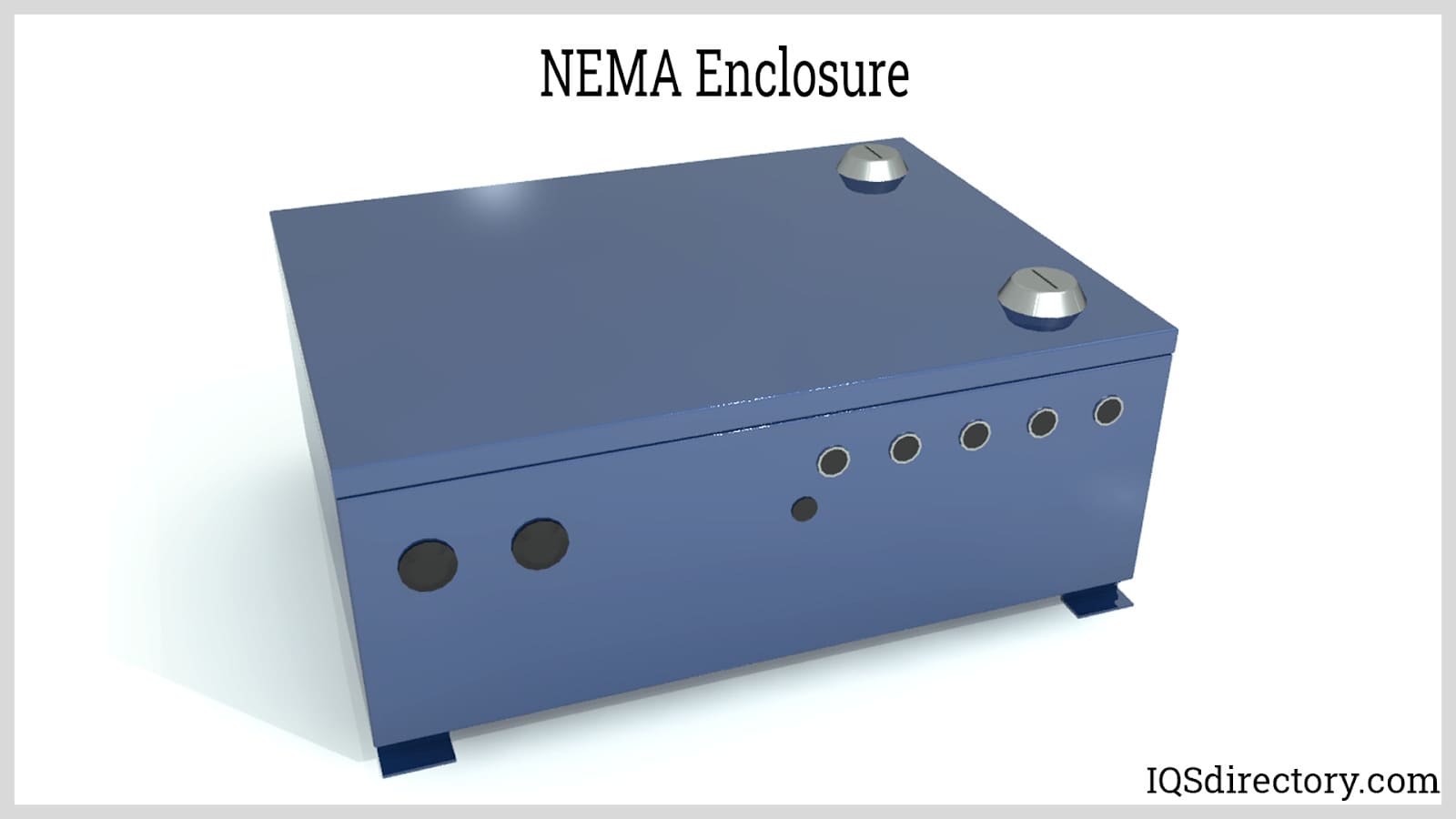
- NEMA Enclosures: Certified by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association, NEMA enclosures are classified by type to indicate protection level against ingress of water, dust, and other hazards. Common ratings include:
- Type 1: Indoor use, basic protection against dust and light debris, suitable for IT closets and utility rooms.
- Type 3R: Outdoor use, protects against rain, sleet, and snow, ideal for telecommunications or power distribution in non-hazardous locations.
- Type 4: Indoor/outdoor use, watertight and dust-tight, suitable for washdown environments, food processing, and industrial automation.
- Type 12: Indoor use, protection against circulating dust, dripping liquids, and non-corrosive contaminants, often used in manufacturing and assembly areas.
- Project Enclosures: Small, versatile housings favored by students, engineers, and electronics hobbyists for prototyping custom circuits and DIY electronics projects. These enclosures are typically made from ABS plastic or polycarbonate for easy machining and modification.
- Stainless Steel Enclosures: Known for their corrosion resistance, heat dissipation, and hygienic surfaces, stainless steel enclosures are widely used in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and marine environments. Their robust construction makes them ideal for high-power applications and outdoor installations requiring a high degree of ingress protection.
- Aluminum Enclosures: Diecast aluminum enclosures provide excellent thermal conductivity, shielding, and mechanical strength. Their lightweight design suits portable equipment and indoor installations, although untreated aluminum is less suitable for high-moisture environments.
- ABS Enclosures: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is a durable, impact-resistant thermoplastic, making it a top choice for handheld, battery-powered devices and portable instrumentation. ABS enclosures offer superior insulation and shock absorption, and are easy to customize for switches, displays, and connectors.
- Polycarbonate Enclosures: These plastic enclosures excel in low-temperature, UV-exposed, or impact-prone environments. Polycarbonate’s electrical insulation and moldability allow for ultra-compact, rugged housings in both indoor and outdoor installations.
- Fiberglass Enclosures: Combining chemical resistance, heat tolerance, and excellent dielectric properties, fiberglass enclosures are preferred for corrosive, wet, or salty environments such as water treatment plants, coastal installations, and chemical processing facilities.
Still unsure which enclosure type is right for your application? Start your search with these questions:
- Do you need indoor or outdoor protection?
- Is EMI shielding or RFI attenuation critical for your electronics?
- Will the enclosure be exposed to chemicals, salt, or extreme weather?
- How important are aesthetics, portability, or modularity?
Design and Customization
Electronic enclosures are available in an extensive range of shapes, sizes, and configurations, with the majority taking on a rectangular or box-like profile for optimized space utilization and stacking efficiency. However, manufacturers also produce round, hexagonal, and custom-contoured housings for unique form factors. Most enclosures feature removable panels or hinged doors, enabling straightforward access to internal components for maintenance, upgrades, or cable management. Sizes range from miniature project boxes for a single PCB to walk-in server rooms and large-scale industrial cabinets.
Materials
The choice of materials for an electronic enclosure is central to its performance and long-term reliability. Common materials and their advantages include:
- Stainless Steel: Outstanding corrosion resistance, non-reactive, suitable for sanitary or harsh environments.
- Aluminum: Lightweight, excellent conductivity, good EMI/RFI shielding, easy to machine and anodize.
- Fiberglass Reinforced Polyester (FRP): Non-conductive, highly resistant to chemicals and UV exposure, ideal for outdoor use.
- Polycarbonate and ABS Plastics: Low weight, high impact resistance, customizable, excellent insulation properties.
- Carbon Fiber and Kevlar: Used in specialty applications requiring extreme strength-to-weight ratios or ballistic protection.
Manufacturers select materials based on a thorough evaluation of the application’s environment, regulatory requirements, and end-user preferences. Key considerations include:
- Corrosion Resistance: Essential for outdoor, marine, or chemical processing installations.
- Thermal Management: For high-power electronics, materials with good heat dissipation properties help prevent overheating.
- EMI/RFI Shielding: Required in sensitive datacom, broadcast, or military applications to prevent signal interference.
- Mechanical Strength and Security: Impact resistance, tamper-proofing, and locking mechanisms deter vandalism and unauthorized access.
- Ingress Protection (IP) Rating: Indicates the enclosure’s effectiveness at excluding water and dust (e.g., IP65, IP67).
Customization Options
Modern manufacturing technologies and CAD software, such as Protocase Designer, allow for highly customized enclosures tailored to unique requirements. Manufacturers can adjust:
- Dimensions and Form Factor: From ultra-compact, wearable IoT device enclosures to oversized industrial cabinets.
- Mounting and Orientation: Desktop, handheld, wall-mounted, or floor-standing designs; vertical or horizontal orientation.
- Access Features: Hinged doors, removable panels, snap-fit lids, and quick-release mechanisms.
- Security Enhancements: Locking handles, tamper-evident seals, alarm integration, and reinforced hinges.
- Thermal Management: Built-in heat sinks, ventilation grilles, active cooling fans, and thermal insulation layers.
- User Interface Accommodation: Cutouts or recesses for LCD screens, keypads, touch panels, and labeling.
- Cable Management: Gland plates, knockouts, cable trays, and strain reliefs for neat, safe wiring.
- Environmental Sealing: Gaskets, O-rings, and advanced joint construction (lap joints, tongue-and-groove) for IP/NEMA compliance.
What customization features does your project require? Consider:
- Do you require branding, silk-screened labels, or color coding?
- Is tool-less access or modular expansion important for your application?
- Will you need integrated power supplies, battery compartments, or data ports?
Safety and Compliance Standards
Purchasing electronic enclosures that adhere to recognized safety and compliance standards is essential for regulatory approval, operational safety, and liability protection. In the United States, the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) assigns enclosure ratings based on their resistance to ingress, corrosion, and impact. For global applications, the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) issues IP (Ingress Protection) ratings, such as IP54, IP65, or IP67, denoting resistance to dust and water.
Key standards and certifying bodies include:
- NEMA – Defines enclosure types for North American markets (e.g., NEMA 4X for washdown and corrosion-resistant applications).
- IEC – International IP code for ingress protection against solids/liquids.
- UL (Underwriters Laboratories): Certifies products for fire safety, electrical hazards, and construction quality.
- CSA (Canadian Standards Association): Enforces safety standards for Canadian markets.
- OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration): Regulates workplace safety for electrical installations.
- NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology): Provides guidelines for performance and interoperability.
When specifying or sourcing an electronic enclosure, always check which standards apply to your application and region. Compliance not only ensures legal operation but also boosts customer confidence and minimizes operational risks.
Things to Consider When Choosing an Electronic Enclosure
Selecting the optimal enclosure for your project involves more than simply matching size and price. Here are critical decision factors to evaluate:
- Environmental Conditions: Will the enclosure face exposure to moisture, chemicals, sunlight, or temperature extremes?
- Level of Protection Required: What are the minimum NEMA or IP ratings needed for compliance and reliability?
- Ease of Installation and Maintenance: Are tool-less entry, clear labeling, and ample space for wiring important?
- Customization Needs: Do you require custom cutouts, branding, or integrated electronics?
- Budget and Lead Time: How do cost, availability, and expected delivery dates align with your project schedule?
- After-Sales Support: Does the manufacturer offer technical support, replacement parts, or customization services?
To streamline your buying process, we recommend compiling a list of requirements—including environmental threats, compliance standards, required features, and service expectations—before engaging with enclosure suppliers. For additional support, browse our curated list of trusted electronic enclosure manufacturers, featuring detailed profiles and contact information.
Are you evaluating multiple suppliers or enclosure designs? Ask yourself:
- Which manufacturer offers the best combination of product quality, support, and price?
- Does the enclosure meet all relevant standards for your industry and location?
- Is the enclosure future-proof—can it be modified or expanded as technology evolves?
Once you have identified top contenders, reach out with a request for quote (RFQ) or schedule a consultation to discuss your specific needs. Compare responses not only by price, but also by communication quality, customization ability, and warranty terms. The right enclosure partner will offer expert guidance, fast turnaround, and flexible solutions tailored to your industry and application.
Benefits of Quality Electronic Enclosures
Investing in a well-designed, standards-compliant electronic enclosure yields long-term benefits, including:
- Enhanced Equipment Protection: Safeguards sensitive electronics from dust, water, EMI, and mechanical impact.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensures adherence to safety and industry standards, avoiding costly fines and delays.
- Improved Safety: Reduces risk of electrical shock, fire, and accidents for personnel and end-users.
- Operational Reliability: Minimizes downtime due to environmental damage or unauthorized access.
- Custom Fit and Aesthetics: Offers tailored designs that match brand image, functional requirements, and installation environments.
- Future-Proofing: Modular, upgradable enclosures accommodate technological advancements and changing requirements.
Looking for more technical resources or a deeper dive into enclosure engineering?
- Explore metal box options for EMI shielding and rugged environments
- Learn more about custom electrical enclosure solutions
- Discover customization possibilities for unique applications
Get Started: Choosing Your Electronic Enclosure
The right electronic enclosure is key to protecting your investment, ensuring compliance, and maintaining operational efficiency. Begin your search by defining your critical requirements—such as IP or NEMA rating, material, size, and special features—and comparing suppliers based on expertise, responsiveness, and ability to deliver both standard and custom solutions.
Ready to take the next step? Browse our comprehensive directory of electronic enclosure manufacturers to connect with industry leaders who prioritize your needs. For help with technical specifications, compliance questions, or customization requests, contact a supplier directly for expert guidance and fast turnaround.
Choosing the proper enclosure is an investment in the performance, safety, and reliability of your electronic systems. By considering application-specific factors and working with a trusted partner, you’ll ensure your electronics are well-protected—today and for years to come.
What is the primary function of an electronic enclosure?
The primary function of an electronic enclosure is to protect sensitive electronic equipment and circuitry from physical hazards, environmental contaminants, and electromagnetic interference (EMI), ensuring reliability and safety across various industries.
Which materials are commonly used for electronic enclosures?
Common materials used for electronic enclosures include stainless steel, aluminum, fiberglass reinforced polyester (FRP), polycarbonate, ABS plastics, and specialty materials such as carbon fiber and Kevlar. The selection depends on application requirements like corrosion resistance, thermal management, and electrical insulation.
What are NEMA and IP ratings for electronic enclosures?
NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) and IP (Ingress Protection) ratings are standards that define an enclosure’s resistance to hazards such as dust, water, and impact. NEMA ratings are primarily used in North America, while IP codes are recognized internationally. Selecting the correct rating ensures compliance and adequate protection for the intended environment.
How do I choose the right electronic enclosure for my application?
Choosing the right enclosure involves evaluating environmental conditions, required level of protection, customization needs, ease of installation, budget, and compliance standards. Consider factors such as exposure to moisture or chemicals, EMI shielding needs, accessibility, and service requirements to ensure optimal equipment protection and regulatory adherence.
What customization options are available for electronic enclosures?
Customization options include adjusting enclosure size and form, choosing mounting styles, adding hinged doors or removable panels, integrating cable management, implementing thermal management solutions, incorporating user interfaces, and applying branding or color coding. Advanced manufacturing allows for tailored solutions to meet unique project requirements.
Why is compliance with safety standards important when selecting an electronic enclosure?
Compliance with recognized safety standards such as NEMA, IEC, UL, CSA, and OSHA ensures operational safety, legal adherence, and reduced liability. Certified enclosures protect against electrical hazards, fire, ingress of water or dust, and help facilitate regulatory approval in various markets and industries.
What are the benefits of investing in a quality electronic enclosure?
A quality electronic enclosure enhances equipment protection, ensures regulatory compliance, improves user and personnel safety, minimizes operational downtime, and offers tailored design and future-proofing options. This investment supports long-term reliability and efficient operation of electronic systems.





 Electric Coils
Electric Coils Electric Switches
Electric Switches Electric Transformers
Electric Transformers Electronic Connectors
Electronic Connectors Electronic Enclosures
Electronic Enclosures EMI Shielding
EMI Shielding Membrane Switches
Membrane Switches Power Cords
Power Cords Static Eliminators
Static Eliminators Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services