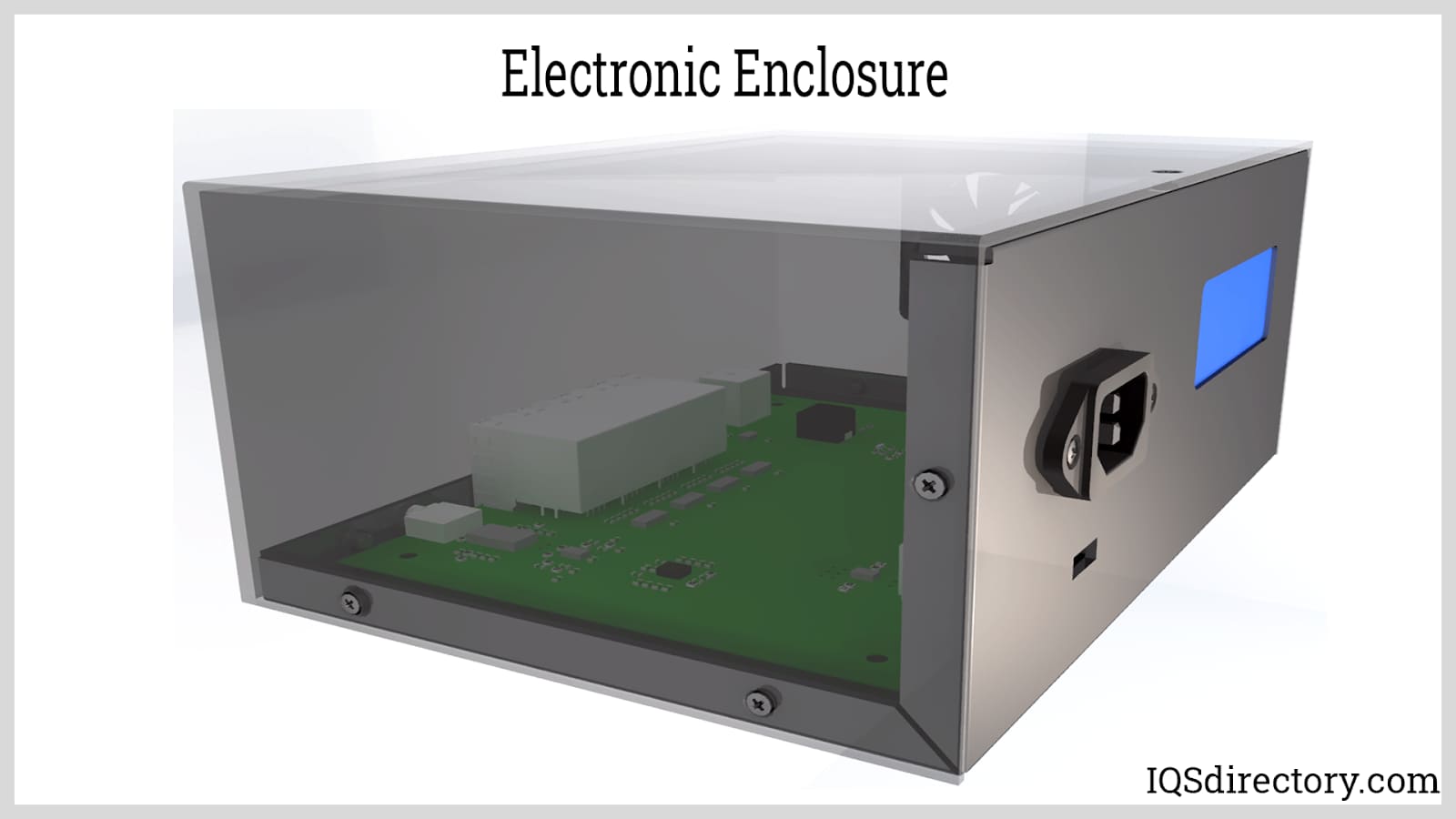
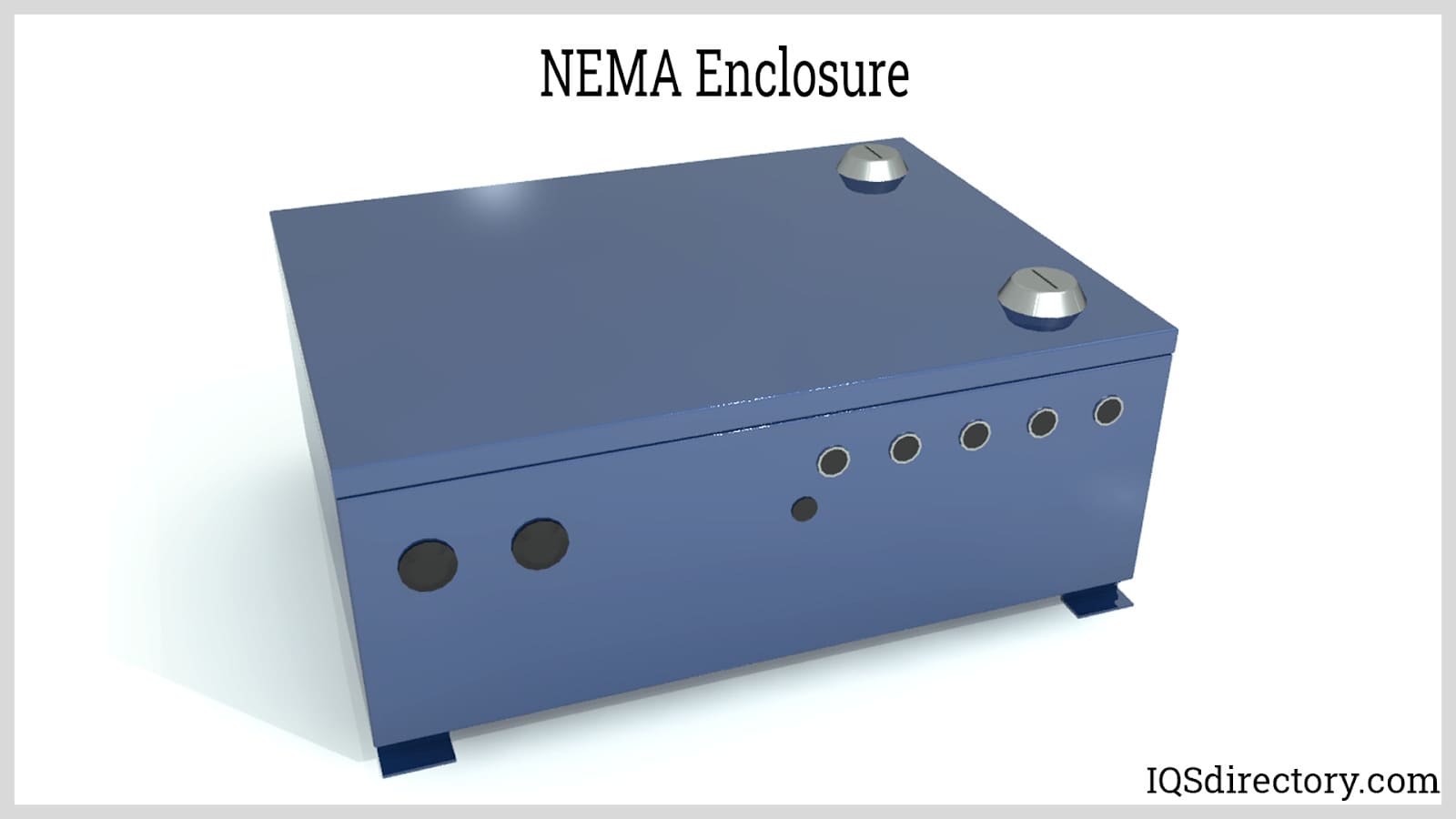
Instrument enclosures protect electronic devices inside metal or plastic housing. Because of their sensitive circuitry, the components must be protected from dirt, water and accidental contact. Being kept in an enclosure prevents the intrusion of solid foreign objects as well as liquids to a certain extent. Instrument enclosures are made from aluminum, acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) plastic, stainless steel and, for certain models, polyester with fiberglass reinforcing. Read More…
At Hubbell Wiegmann, we specialize in designing and manufacturing high-quality electronic enclosures that protect and support a wide range of industrial and commercial systems. We bring decades of engineering expertise to every product we create, ensuring that our enclosures meet rigorous performance standards while adapting to the evolving needs of our customers.
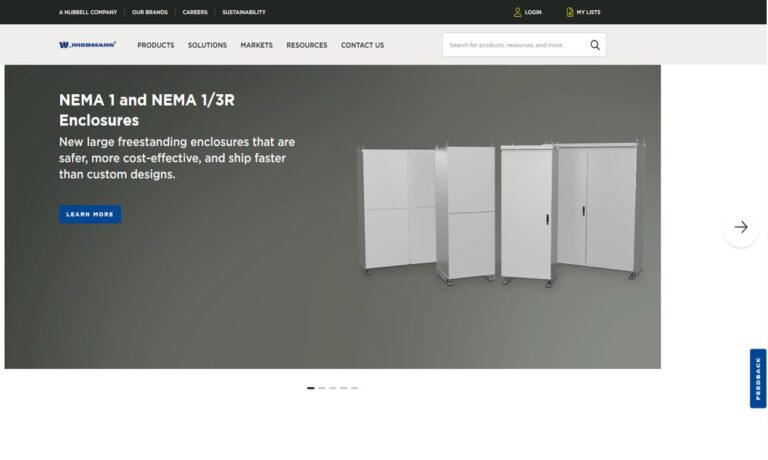
AutomationDirect.com takes pride in being a trusted partner for businesses seeking reliable electronic enclosure solutions. Our team is dedicated to providing exceptional customer service and technical support to ensure that our customers find the perfect products to meet their needs.
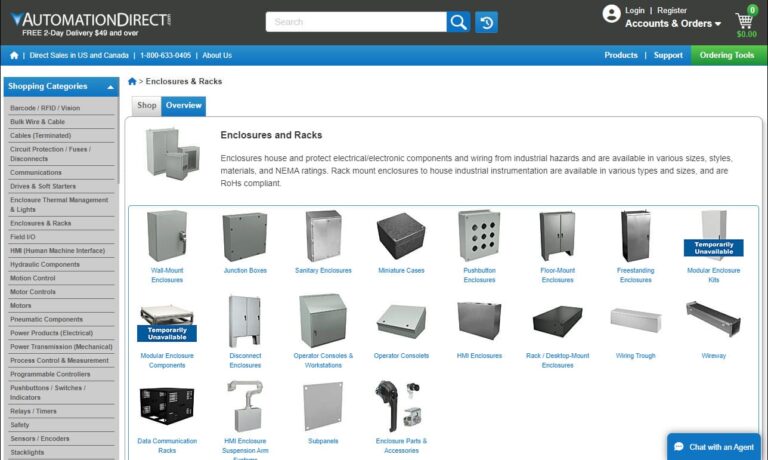
At Ometek Inc., we specialize in designing and manufacturing high-quality industrial electronic enclosures for a wide range of applications. Our team of skilled engineers and technicians has years of experience in the industry, and we are committed to delivering the most reliable and durable enclosures to our customers.
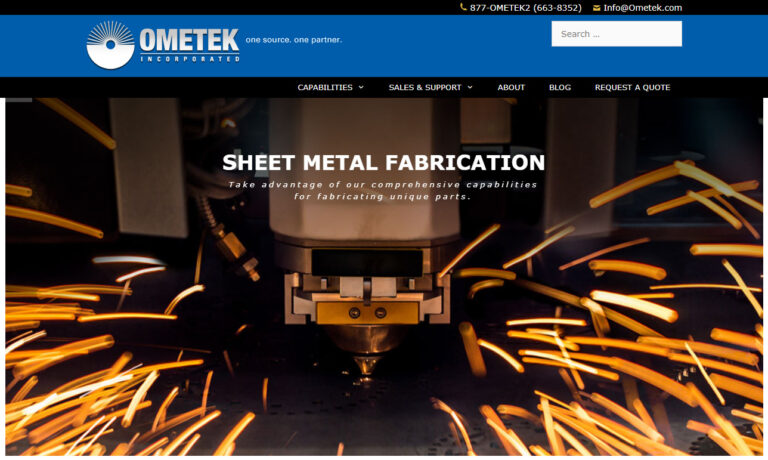
At Accurate Metal Fabricating, we specialize in crafting precision-engineered electronic enclosures that meet the unique demands of modern industries. With a relentless commitment to quality, we pride ourselves on providing cutting-edge enclosures that safeguard electronic components with unparalleled accuracy. At the heart of our success is a passion for innovation, driving us to create...
At Bison ProFab, we specialize in designing and manufacturing high-quality electronic enclosures that deliver superior protection in the most demanding environments. We take pride in our ability to engineer enclosures that meet rigorous industry standards while adapting to the specific needs of our customers across a broad range of applications.

More Instrument Enclosure Manufacturers
Instrument Enclosures: Comprehensive Guide to Types, Applications, and Selection Criteria
Instrument enclosures are essential for safeguarding sensitive electronic instruments and components from environmental hazards, mechanical impact, and interference. Available in a diverse range of configurations, instrument enclosures are specifically engineered to accommodate the unique requirements of various devices. Whether you need compact, ergonomically designed handheld enclosures or robust, industrial-grade wall mount enclosures, selecting the right enclosure is crucial for functionality, safety, and regulatory compliance.
What Are Instrument Enclosures?
Instrument enclosures are protective housings designed to shield electronic instruments and circuitry from dust, dirt, moisture, chemicals, electromagnetic interference (EMI), radio frequency interference (RFI), and physical damage. These enclosures are indispensable in sectors such as industrial automation, laboratory research, medical device manufacturing, telecommunications, and process control, where the performance and longevity of electronic components are critical.
Types of Instrument Enclosures
Instrument enclosures come in many varieties to accommodate the wide array of electronic instruments. For small handheld instruments, enclosures may be custom-contoured to the shape of the device and designed to provide long-lasting protection and shock absorption. Desktop instruments can generally be housed in a box-like enclosure that is manageable in size and durability, protecting against spills and accidental contact.
- Handheld Enclosures: Ideal for portable devices, handheld enclosures feature ergonomic designs, shock-absorbing materials, and optional cutouts for displays or buttons. Common applications include remote controls, portable testers, and medical diagnostic tools.
- Desktop Enclosures: These are typically used for benchtop instruments, power supplies, or data acquisition systems. Desktop enclosures offer features such as easy access panels, ventilation slots, and integrated handles for mobility.
- Wall Mounted Enclosures: Wall mounted enclosures keep their contents close to the electronic equipment the instruments control while shielding them from dust, dirt, splashing water and other undesirable contact. Wall mount models are widely used in industrial automation, control panels, and security systems.
- Rackmount Enclosures: Designed for mounting in standard 19-inch racks, these enclosures are common in data centers, telecommunications, and audio-visual equipment.
- DIN Rail Enclosures: Frequently used for modular automation and control equipment, these enclosures snap easily onto DIN rails for efficient installation and maintenance.
- Custom Enclosures: For highly specialized applications, custom instrument enclosures can be engineered with unique dimensions, materials, and features tailored to exact requirements.
Key Features and Components of Instrument Enclosures
The parts of an instrument enclosure vary depending on the application. Handheld enclosures may have slide-on covers or a knockout for an LCD screen. Desktop enclosures may have vents, handles, locking mechanisms and membrane keyboards, while wall mounted enclosures are frequently hung on DIN rail with the ability to slide into position.
When selecting an instrument enclosure, consider features such as:
- Ingress Protection: Seals and gaskets (such as neoprene or silicone) for dust and water resistance, often rated by IP (Ingress Protection) or NEMA standards.
- Material Options: Metal, aluminum, plastic, polycarbonate, fiberglass, or composite materials, each offering different advantages in terms of strength, weight, cost, and corrosion resistance.
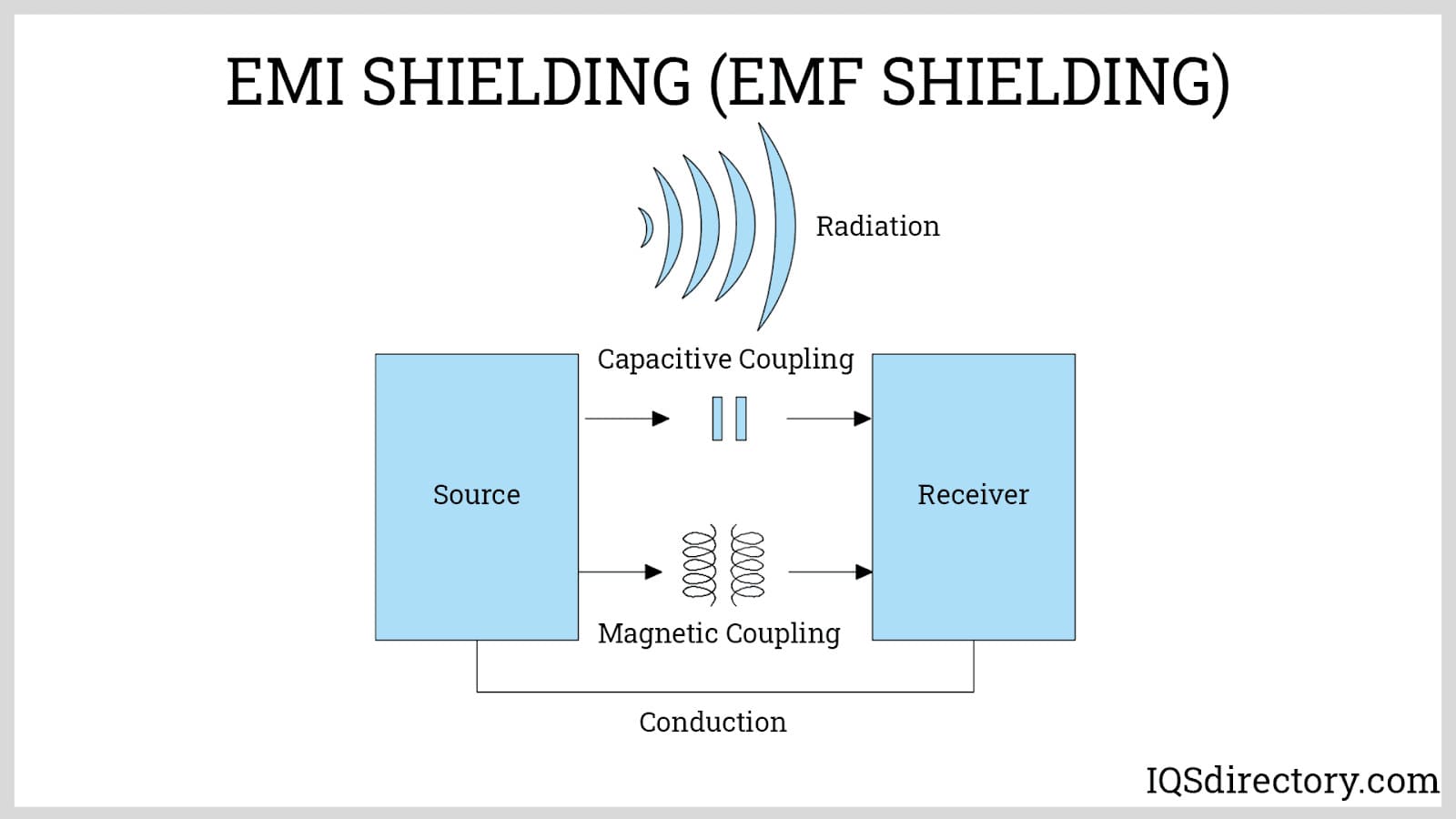
- EMI/RFI Shielding: Special coatings or construction to minimize electromagnetic or radio frequency interference, ensuring reliable operation in electrically noisy environments.
- Thermal Management: Vents, fans, heat sinks, or insulation to manage heat dissipation for temperature-sensitive electronics.
- Access and Security: Hinged or removable covers, lockable doors, cylinder catches, and lock covers to prevent unauthorized access and facilitate maintenance.
- Customization: Transparent lids or covers for display visibility, recessed areas for labels or keypads, and knockouts for connectors or cable glands.
- Environmental Protection: Drain holes, air dryers, and coatings for chemical, UV, or weather resistance.
Other options incorporate neoprene seals or watertight gaskets, transparent lids or covers, recessed areas for labels or keypads, cylinder catches, lock covers, thermometers, drains, air dyers and special coatings to shield the contents from static electricity or EMI/RFI (electromagnetic and radio frequency interference). Metal enclosures can be constructed of cold rolled sheet metal that is welded for a smooth seam; aluminum is usually extruded.
Materials Used in Instrument Enclosures
Choosing the right enclosure material is essential for optimal performance, longevity, and protection. Common materials include:
- Metal Enclosures: Steel and aluminum enclosures offer superior strength, EMI/RFI shielding, and are ideal for harsh industrial environments. Aluminum is lightweight and corrosion-resistant, making it suitable for marine and outdoor applications.
- Plastic Enclosures: High-impact polycarbonate, ABS, and other plastics provide lightweight, cost-effective solutions with good chemical resistance. Plastics are often used for handheld and desktop enclosures where weight and aesthetics are priorities.
- Fiberglass and Composite Enclosures: These materials are gaining favor in certain situations because of their corrosion resistance, durability and weight. Fiberglass is particularly valued for its ability to withstand corrosive chemicals and UV exposure, making it a top choice for outdoor and industrial settings.
No matter what the material is, however, there are certain standards to which all enclosures must adhere. NEMA, the National Electrical Manufacturers Association, UL, the Underwriters Laboratories and the IP Code, or the International Protection Rating are all used to identify the enclosure's strengths and applicable functions as determined by the conditions they can withstand. For example, the common NEMA Type 4X enclosure can be used indoors or outdoors to protect its contents against corrosion, windblown dust, rain, sleet, snow, splashing or hose-directed water and the external formation of ice.
Industry Standards and Certifications for Instrument Enclosures
Instrument enclosures must comply with industry standards to ensure safety, performance, and reliability. Major certification and rating systems include:
- NEMA Ratings: Define levels of protection against environmental hazards such as dust, water, and corrosion. Common types include NEMA 1, 3R, 4, 4X, and 12.
- IP Ratings: The Ingress Protection (IP) Code classifies enclosures based on their resistance to solid particles and liquids (e.g., IP65, IP66, IP67).
- UL Certification: Underwriters Laboratories test and certify enclosures for safety, flammability, and performance.
- CE Marking: For products sold in the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates compliance with relevant health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
Curious about which enclosure rating is best for your application? Explore our guide: Choosing the Right NEMA and IP Rated Enclosure.
Applications and Use Cases for Instrument Enclosures
Instrument enclosures are used in a wide range of industries and settings, with specific designs and features tailored to each use case. Common applications include:
- Industrial Automation: Housing for programmable logic controllers (PLCs), motor drives, and human-machine interfaces (HMIs).
- Medical Devices: Protection for diagnostic equipment, patient monitors, and portable analyzers, ensuring compliance with hygiene and safety standards.
- Test and Measurement Equipment: Enclosures for oscilloscopes, multimeters, and signal generators, where durability and EMI shielding are critical.
- Telecommunications: Racks and cabinets for networking, signal processing, and broadband equipment.
- Laboratory and Scientific Research: Enclosures for sensors, data loggers, and analytical instruments requiring controlled environments.
- Energy and Utilities: Weatherproof enclosures for monitoring systems, smart meters, and control panels in power generation and distribution.
- Consumer Electronics: Housings for audio equipment, smart home devices, and personal gadgets.
Benefits of High-Quality Instrument Enclosures
Investing in the right instrument enclosure delivers numerous advantages, including:
- Protection from Environmental Hazards: Enclosures safeguard sensitive electronics from dust, moisture, chemicals, and mechanical impact, extending equipment lifespan.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting NEMA, IP, and UL standards ensures your equipment adheres to safety and industry regulations.
- EMI/RFI Shielding: Prevents signal interference and data corruption, especially crucial for measurement and control devices.
- Thermal Management: Designed features help dissipate heat and maintain optimal operating temperatures for critical electronics.
- Customization and Branding: Tailored enclosures can incorporate company logos, colors, and unique features for product differentiation.
- User Accessibility: Well-designed enclosures enhance device usability, allowing convenient access for maintenance and operation.
Wondering how a high-quality enclosure can improve your product reliability? Contact our team for a free consultation or request a customized quote.
How to Select the Right Instrument Enclosure
Choosing the best instrument enclosure involves careful evaluation of several factors. Consider the following decision points as you review enclosure options:
- Environmental Conditions: Will the enclosure be exposed to moisture, chemicals, extreme temperatures, or UV light?
- Size and Form Factor: What dimensions, mounting options, and space constraints must be accommodated?
- Material Selection: Which material offers the balance of durability, weight, cost, and required certifications?
- Regulatory Requirements: What NEMA, IP, UL, or CE certifications are necessary for your application or market?
- Thermal and EMI/RFI Management: Does your device require special provisions for cooling or shielding?
- Access, Security, and Customization: Will you need lockable doors, transparent panels, or custom branding?
- Production Volume and Lead Time: Are standard off-the-shelf enclosures sufficient, or is a custom solution required?
Need help narrowing your options? Ask our experts: What enclosure is best for industrial automation? Which materials are ideal for outdoor applications? How do I ensure regulatory compliance? Get answers to your enclosure questions.
Customization and Value-Added Services
Many enclosure manufacturers provide a range of customization services to help you achieve a perfect fit and finish for your project, including:
- CNC Machining and Cutouts: Precise openings for connectors, switches, displays, and cable glands.
- Printing and Labeling: Company branding, safety instructions, and operational graphics applied directly to the enclosure.
- Surface Finishing: Powder coating, anodizing, painting, and texturing for improved appearance and durability.
- Assembly and Integration: Pre-installed hardware, gaskets, cable management, and sub-assembly integration to streamline your production process.
- Prototyping and Short Runs: Rapid prototyping and low-volume production for development and testing phases.
Do you require a custom enclosure design or unique features for your application? Explore our custom enclosure capabilities to learn more.
Trends and Innovations in Instrument Enclosure Design
The demand for advanced enclosure solutions continues to grow as industries adopt new technologies and face evolving regulatory requirements. Current trends in instrument enclosure design include:
- Smart Enclosures: Integration of sensors, IoT connectivity, and real-time monitoring to enable predictive maintenance and remote diagnostics.
- Sustainable Materials: Use of recyclable plastics, bio-based composites, and eco-friendly coatings to reduce environmental impact.
- Modular and Scalable Designs: Enclosures that can be easily expanded or reconfigured to accommodate evolving equipment requirements.
- Enhanced Security Features: Built-in electronic locks, tamper detection, and access logging for high-security environments.
- Improved Thermal Solutions: Advanced passive and active cooling systems for increasingly powerful electronics.
Frequently Asked Questions About Instrument Enclosures
- What is the difference between NEMA and IP ratings? NEMA ratings are primarily used in North America and address protection against specific environmental conditions, while IP ratings are internationally recognized and describe protection against solids and liquids.
- Can enclosures be customized for unique device shapes or features? Yes, many manufacturers offer full customization, including size, cutouts, finishes, and branding to meet your exact requirements.
- Are plastic enclosures suitable for outdoor use? Certain plastics, such as UV-stabilized polycarbonate and fiberglass-reinforced polyester, are well-suited for outdoor environments due to their durability and resistance to weathering.
- How do I select an enclosure for EMI/RFI shielding? Choose enclosures made from conductive metals or those with special shielding coatings, and ensure proper gasket and grounding design for optimal EMI/RFI protection.
- What value-added services are available from enclosure manufacturers? Services may include CNC machining, powder coating, silk-screen printing, assembly, and kitting for a turnkey solution.
Still have questions? Contact our enclosure specialists for personalized assistance.
Conclusion: Why Instrument Enclosure Selection Matters
Instrument enclosures are far more than simple boxes—they are vital to the safety, performance, and reliability of electronic equipment across countless industries. By understanding enclosure types, materials, standards, and customization options, you can make informed decisions that protect your investment and meet project demands. Whether your priority is durability, regulatory compliance, EMI/RFI shielding, or aesthetics, there is an enclosure solution tailored to your needs.
Ready to take the next step? Request a fast quote or speak with a technical advisor to discuss your instrument enclosure project today.







 Electric Coils
Electric Coils Electric Switches
Electric Switches Electric Transformers
Electric Transformers Electronic Connectors
Electronic Connectors Electronic Enclosures
Electronic Enclosures EMI Shielding
EMI Shielding Membrane Switches
Membrane Switches Power Cords
Power Cords Static Eliminators
Static Eliminators Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services